函数地图 变量操作 分类 功能 函数 因子 因子重编码 forcats::fct_recode 因子 因子逆序 …

何凌锋的个人主页 & 分享平台

函数地图 变量操作 分类 功能 函数 因子 因子重编码 forcats::fct_recode 因子 因子逆序 …

WinUI 3本身未提供任务视图图标接口,可通过WinUI.WinUIEx包实现。下列代码省略命名空间声明;C …

The human social and behavioral activities play significant roles in the spread of COVID-19. Social-distancing centered non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) are the best strategies to curb the spread of COVID-19 prior to an effective pharmaceutical or vaccine solution. This study investigates various social-distancing measures’ impact on the spread of COVID-19 using advanced global and novel local geospatial techniques. Social distancing measures are acquired through website analysis, document text analysis, and other big data extraction strategies. A spatial panel regression model and a newly proposed geographically weighted panel regression model are applied to investigate the global and local relationships between the spread of COVID-19 and the various social distancing measures. Results from the combined global and local analyses confirm the effectiveness of NPI strategies to curb the spread of COVID-19. While global level strategies allow a nation to implement social distancing measures immediately at the beginning to minimize the impact of the disease, local level strategies fine tune such measures based on different times and places to provide targeted implementation to balance conflicting demands during the pandemic. The local level analysis further suggests that implementing different NPI strategies in different locations might allow us to battle unknown global pandemic more efficiently.

The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns have created immeasurable health and economic crises, leading to unprecedented disruptions to world trade. The COVID-19 pandemic shows diverse impacts on different economies that suffer and recover at different rates and degrees. This research aims to evaluate the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of international trade network vulnerabilities in the current crisis to understand the global production resilience and prepare for the future crisis. We applied a series of complex network analysis approaches to the monthly international trade networks at the world, regional, and country scales for the pre- and post- COVID-19 outbreak period. The spatio-temporal patterns indicate that countries and regions with an effective COVID-19 containment such as East Asia show the strongest resilience, especially Mainland China, followed by high-income countries with fast vaccine roll-out (e.g., U.S.), whereas low-income countries (e.g., Africa) show high vulnerability. Our results encourage a comprehensive strategy to enhance international trade resilience when facing future pandemic threats including effective non-pharmaceutical measures, timely development and rollout of vaccines, strong governance capacity, robust healthcare systems, and equality via international cooperation. The overall findings elicit the hidden global trading disruption, recovery, and growth due to the adverse impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.

The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns have created immeasurable health and economic crises, leading to unprecedented disruptions to world trade and supply chains. The COVID-19 pandemic shows diverse impacts on different economies and markets that suffer and recover at different rates and degrees. This research aims to evaluate the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of strengths and vulnerabilities of international trade networks in the current crisis to understand the global production resilience and prepare for the future crisis. We applied a series of complex network analysis approaches to the monthly international trade networks at the world scale, regional scale, and country scale for the pre- and post- COVID-19 outbreak period from 2018 to 2021. The spatio-temporal patterns indicate that countries and regions with an effective COVID-19 containment such as East Asia show the strongest resilience, especially mainland China, followed by high-income countries (e.g., European Union), whereas low-income countries (e.g., Africa) show high vulnerability. The overall findings elicit the hidden global trading disruption, recovery, and growth due to the adverse impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Social eating – or eating a meal with significant others – is universally important for social networking in society. This article reviews a research program on social eating as a network builder and resource mobilizer for favor exchanges, and presents new survey evidence on patterns of participation in social eating and favor exchanges in China today.
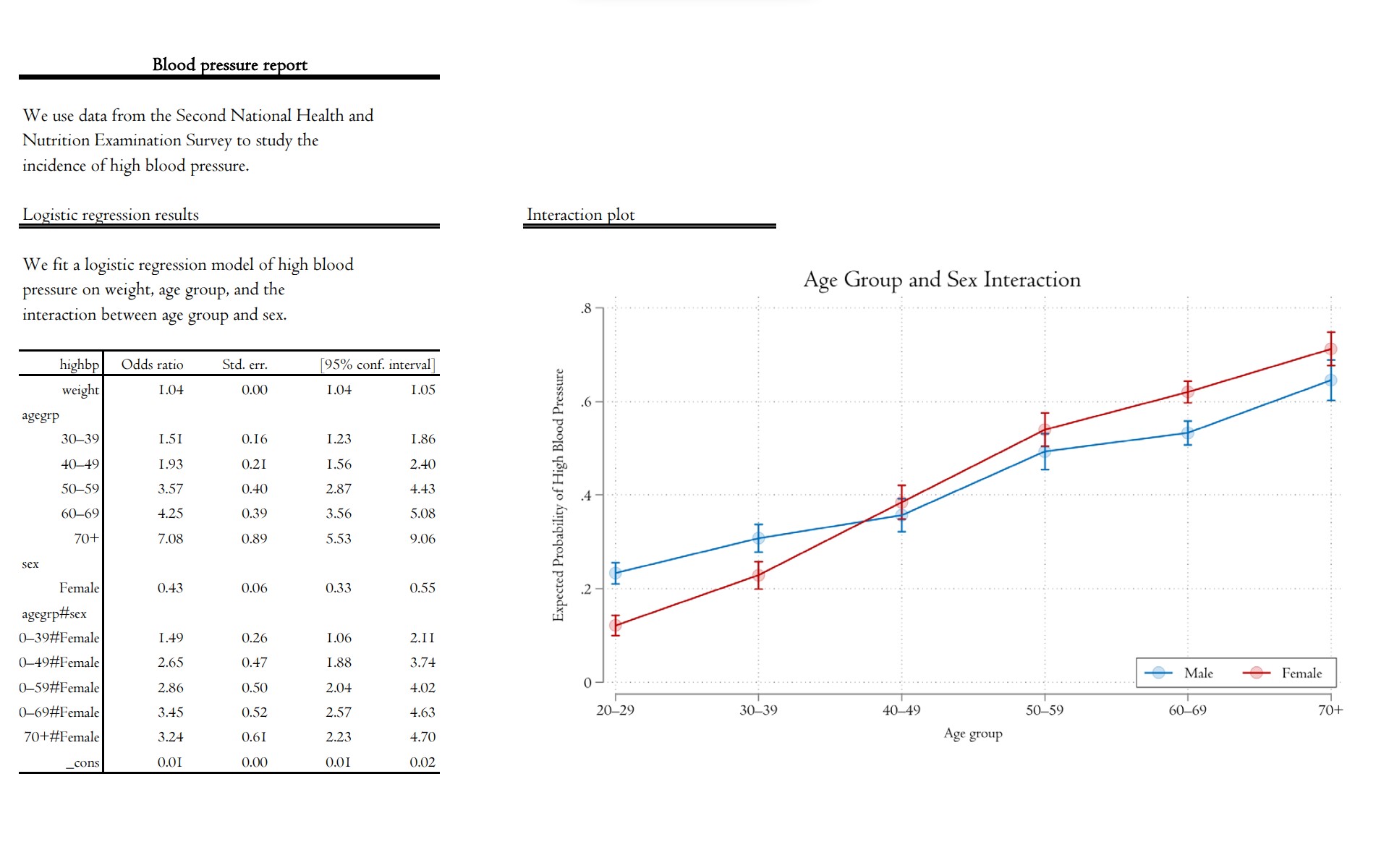
使用Stata自动化生成包括格式化文本、统计信息、回归结果和图形的Word®、Excel®、PDF和HTML文档。文档翻译自:Truly reproducible reporting | New in Stata 16。
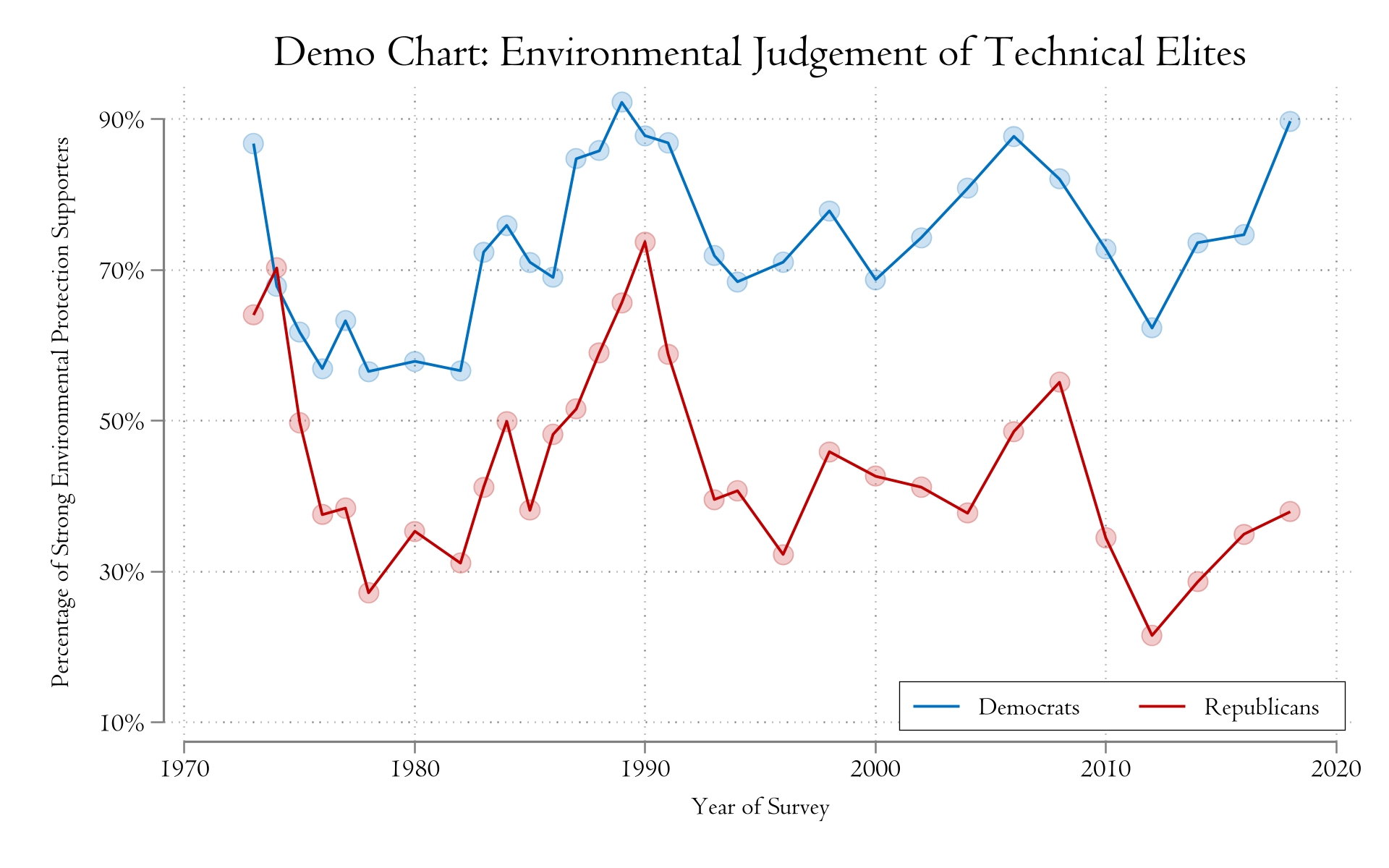
Stata绘图配色方案设置。

The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns have created health and economic crises, leading to unprecedented disruption to world trade and supply chains. The COVID-19 shows diverse impacts on different economies and markets that suffer and recover at different rates and degrees. This research aims to evaluate the strengths and vulnerabilities of international trade networks (ITNs) in the current crisis to evaluate global production resilience and prepare for the future crisis. We applied a series of complex network analysis approaches on the monthly ITNs for the pre- and post- COVID-19 outbreak period. The overall findings elicit the hidden spatio-temporal trading disruption, development, and resilience due to the adverse impact of COVID-19 pandemic.
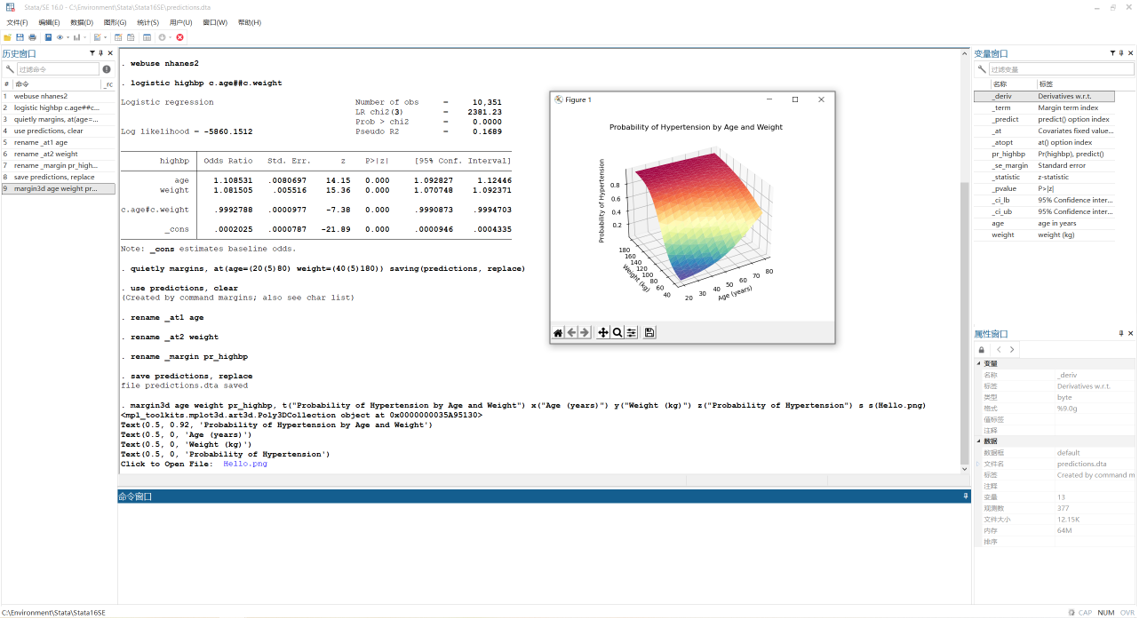
自定义Stata绘制3D边际图命令margin3d,适用于展示两个连续变量的交互作用。